Table of Contents
stock market

Imagine you’re at a market. People are buying and selling fruits, veggies, and other goods. Now, replace the fruits and veggies with pieces of companies. That’s the stock market in simple terms.
Companies sell “shares” of themselves. When you buy a share, you’re basically buying a tiny piece of that company and basically becoming a owner of the company. And just like at the market, the price of these shares can go up or down depending on demand.
.

What is stock market?
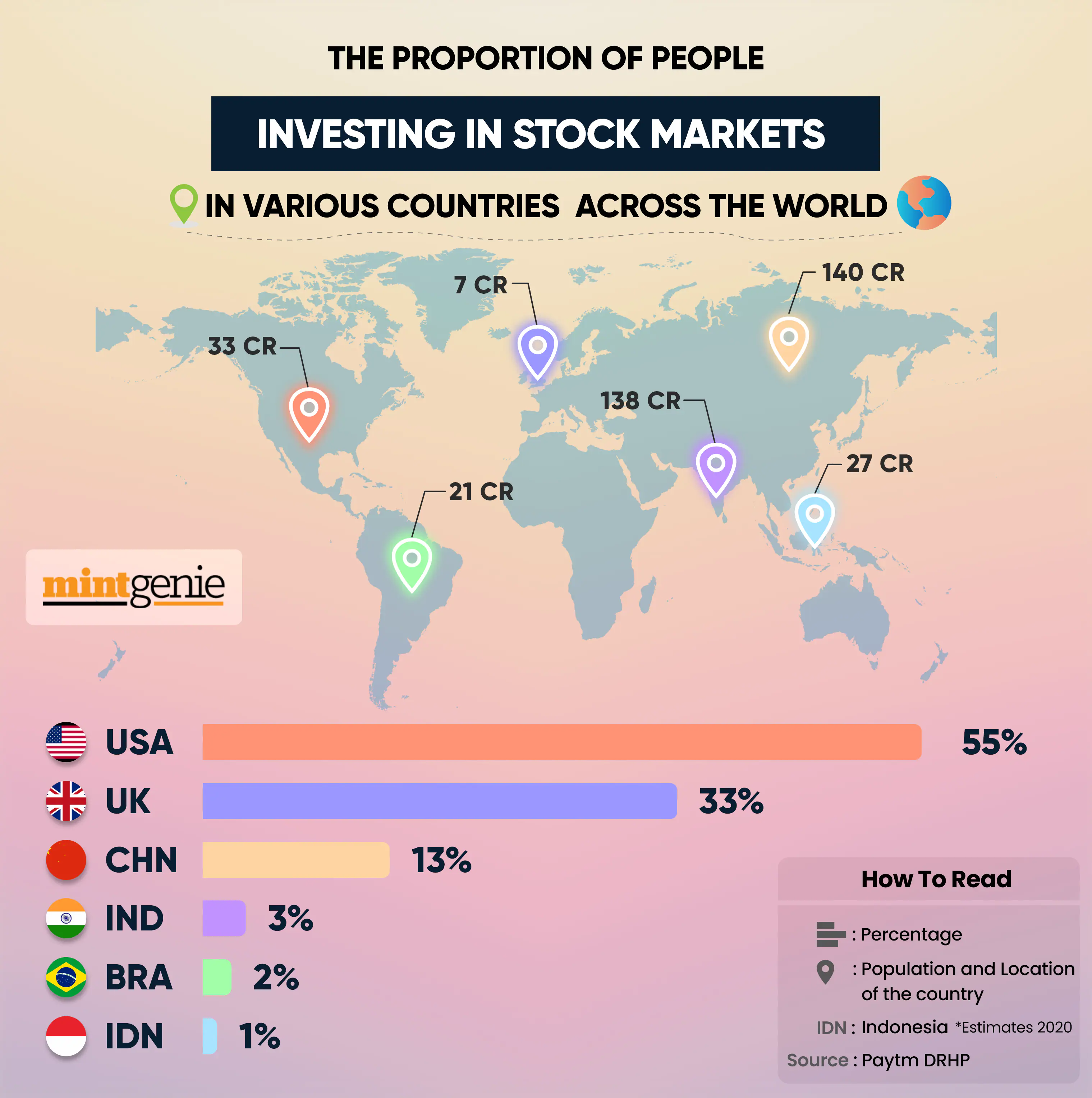
The stock market is where you can buy and sell parts of companies called shares. Many people have made a lot of money from the stock market, but surprisingly, only 1.2 crore Indians out of a population of 138 crore are investing or trading in it.
In simple terms, the share market is a place where you can trade stocks or shares, which are small pieces of a company. In India, most trading happens on two major exchanges: Sensex (Bombay Stock Exchange) and NIFTY (National Stock Exchange). The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) keeps an eye on things to ensure everything runs smoothly and fairly.

Learn to invest in it
Imagine this: you’re in a boxing ring. Now, picture the ring filled with legendary boxers like Mike Tyson, Floyd Mayweather, Muhammad Ali, and Manny Pacquiao. Sounds terrifying, right? This is what trading in the stock market can feel like. You’re up against some seriously experienced traders! So, before you jump in, let’s get you prepared .
Types of Trading: The Basics
Stock market trading can be divided based on two things: how long you hold your trades and the techniques you use. Here’s a quick rundown:
1. Scalping
Think of scalping as speed dating. It’s all about short, quick trades. You hold stocks for just a few minutes and aim to make small profits from lots of trades. Only pros should try this, though—beginners, steer clear!
2. Day Trading
Day trading, or intraday trading, means you buy and sell stocks within the same day. It’s like a daily race: buy low in the morning, sell high before the day ends. If you bought 1,000 shares at $200 and sold them at $225, you’d make a neat $25,000! But if the price drops, well, you lose money just as fast.
3. Positional Trading
This is for those who don’t want to be glued to their screens all day. You hold stocks for a few days or weeks. It’s less intense and more like a mini-vacation in trading terms.
4. Investment
If you’re in it for the long haul, like months or years, you’re investing. There are two main approaches:
- Fundamental Analysis: Looking at a company’s health—its management, products, earnings, etc.
- Technical Analysis: Analyzing past stock prices and charts.
Different Trading Techniques

1. Breakout Trading
Imagine a stock price is like a kid trying to jump over a fence. Once it finally jumps (breaks the resistance level), traders jump in too, hoping for a good ride up.
2. Price Action Trading
This is like playing detective with price movements. Traders watch prices and volumes closely and make decisions based on that, ignoring fancy technical indicators.
3. Swing Trading
Think of swing trading like a swing at the park. You get in when the swing is low (support level) and get out before it swings back down (resistance level).
4. Indicator Trading
Some traders use specific tools (indicators) to guide their trades. It’s like using a map on a road trip to avoid getting lost.
Trading Instruments: Tools of the Trade
You can trade with:
- Equity: Buying shares directly.
- Futures: Agreeing to buy/sell at a set price in the future.
- Options: Buying the right to buy/sell at a set price.
Let’s say you have $3,300 and ACC’s stock is at $1620. If it goes up 5% in two days, here’s how different instruments can make you money:
- Equity: Buy 203 shares, profit about $1644.
- Futures: Buy 500 shares, profit $4050.
- Options: Buy 7500 shares of a call option, profit about $24,300 (but it’s riskier).
Elevate Your Trading Skills in 10 Simple Steps

| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Read Good Books | Start with basics, then dive deeper. |
| Study Charts | Relate what you read to real market charts. |
| Find Your Style | Choose between intraday, positional, swing, or price action trading. |
| Deep Dive | Once you choose, study it thoroughly. |
| Build a System | Decide your entry, stop-loss, and profit points. |
| Backtest | Check your system against past data. |
| Start Trading | But risk only 1-2% of your capital per trade. |
| Learn from Mistakes | They are valuable lessons. |
| Avoid Repeating Mistakes | Make adjustments as needed. |
| Stay Persistent | Trading is a skill that needs focus and dedication. |
Should you leave your job for it?

Before quitting your day job to trade full-time, consider these points:
- Zero Debts: No monthly loan payments that add stress.
- Savings: Enough to cover a year’s expenses.
- Consistent Results: Make sure you’ve had steady profits for at least six months.
- Sufficient Capital: Ensure you have enough trading capital.
- Discipline: Treat trading like a business, with clear goals and plans.

Trading can seem like facing a ring full of boxing legends, but with preparation and practice, you can hold your own. Happy trading, and may your investments be ever in your favor!
FAQs
What is the stock market in simple words?
The stock market is a place where people buy and sell shares of companies. Think of it as a big marketplace where you can trade pieces of ownership in companies. When you buy a share, you own a small part of that company.
How do stocks work?
Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you own a share of that company. Companies issue stocks to raise money for growth and operations. The value of stocks can go up or down based on how well the company performs and other factors, affecting your potential profit or loss.
What is an example of a stock market?
An example of a stock market is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in the U.S. or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) in India. These are platforms where shares of companies are bought and sold.
What are the four types of share markets?
- Primary Market: Where new shares are issued and sold for the first time through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs).
- Secondary Market: Where existing shares are traded among investors (e.g., NYSE, NASDAQ).
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Market: Where stocks not listed on major exchanges are traded directly between parties.
- Derivatives Market: Where contracts based on stocks and other assets are traded, like options and futures.
How to buy and sell shares?
- Open a Brokerage Account: Choose a broker or online trading platform and open an account.
- Research Stocks: Decide which stocks you want to buy based on research and analysis.
- Place an Order: Use the brokerage platform to place a buy order for the stocks you want.
- Monitor and Sell: Keep an eye on your stocks and sell them when you decide it’s the right time or when you need to.
What are 5 stock markets?
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
- NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations)
- London Stock Exchange (LSE)
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)
- Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
Which country is No. 1 in the stock market?
The United States is considered No. 1 in the stock market due to its large and influential exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ, which have some of the world’s largest and most well-known companies.
Can I buy 5 shares of stock?
Yes, you can buy 5 shares of a stock if you have enough money to cover the cost and the stock is available for trading. Most brokerage accounts allow you to purchase as few as one share or as many as you want.
What is 500 stocks?
The term “500 stocks” typically refers to a collection of 500 different stocks or shares. It could also mean the S&P 500 Index, which tracks the performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the U.S., representing a broad section of the American economy.
Latest episodes